Paratuberculosis PCR Kit
Bio-T kit® Mycobacterium avium paratuberculosis
The Paratuberculosis PCR kit is a ready-to-use kit for the quantification and detection of Mycobacterium avium paratuberculosis (MAP) by real-time PCR, for the diagnosis of Paratuberculosis in cattle. This MAP PCR test contains an exogenous IPC internal positive control.
✔ Paratuberculosis duplex PCR kit developed in compliance with French standard U47-600-2 (AFNOR)
✔ Rapid thawing of the ready-to-use, blue-colored Master Mix for easy distinction
✔ Reliable detection of MAP by real-time PCR using exogenous IPC to ensure high-quality results on all matrices, even the most difficult ones
✔ Matrices: feces, slurry, manure, methanizer digestate, ileocaecal valve, whole blood on a heparinized tube, milk. Individual analyses or mixtures of up to 5 depending on the matrix.
✔ Kit developed on AriaMx™ (Agilent Technologies, Fast ramping by default) and confirmed on ABI PRISM® 7500 Fast (Applied Biosystems) in standard and Fast ramping. It is also validated on Mic. For other thermal cyclers, don't hesitate to contact our technical support.
✔ Kit validated on Mic qPCR cycler (Bio molecular systems) with 40 min run
✔ Extraction and amplification program common to all kits for Ruminant species
✔ French manufacturing
- Method
- qPCR
- Species
- Ruminants
- Pathogen
- Mycobacterium avium paratuberculosis
- Brand
- Biosellal
You must be logged to access the documents
Log in to your customer accountResources
Download our marketing documents below for more information.
About Paratuberculosis
Bovine paratuberculosis, also known as Johne's disease, is a chronic bacterial infection mainly affecting cattle. The disease is caused by Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP), a bacterium that infects the intestinal tract of animals. Symptoms of bovine paratuberculosis include chronic diarrhea, weight loss, reduced milk production, and increased mortality in infected animals.


Diagnosis & prevention of paratuberculosis
DIAGNOSIS
Paratuberculosis is often difficult to diagnose, due to its slow progression and similarity to other gastrointestinal diseases. Early diagnosis of Bovine Paratuberculosis is crucial for effective control measures. Paratuberculosis real-time PCR and digital PCR kits, such as those developed by BioSellal, offer a rapid and accurate solution for the detection of MAP (Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis) in animal samples, as well as environmental samples such as manure and soil scrapings.
PREVENTION
➜ Herd Management: Separation of infected or suspect animals from the rest of the herd, use of clean, dry bedding, and hygienic feeding practices to reduce animal exposure to the bacteria.
➜ Screening tests: performance of individual and pooled serological tests, as well as DNA detection to identify infected or carrier animals with MAP, elimination of infected or carrier animals from the herd to reduce the spread of the disease.
➜ Hygiene and bio-security: cleaning and disinfecting facilities and equipment to reduce environmental contamination by MAP, limiting the introduction of animals from infected or high-risk herds.
In summary, Johne's disease prevention relies on a combination of herd management practices, testing, control programs, hygiene, and biosecurity. An integrated approach is essential to reduce the prevalence of the disease and minimize its impact on animal health and herd productivity.
Discover all our solutions for optimal paratuberculosis diagnosis
How can you use our solutions to address your field challenges?
Made in France
Opt for quality and local know-how.
Iso-certified
A guarantee of quality in line with international standards.
Secure payment
Your transactions are completely secure.
Availability & support
Our technical support team is on hand to help you with your analyses.
Frequently asked questions
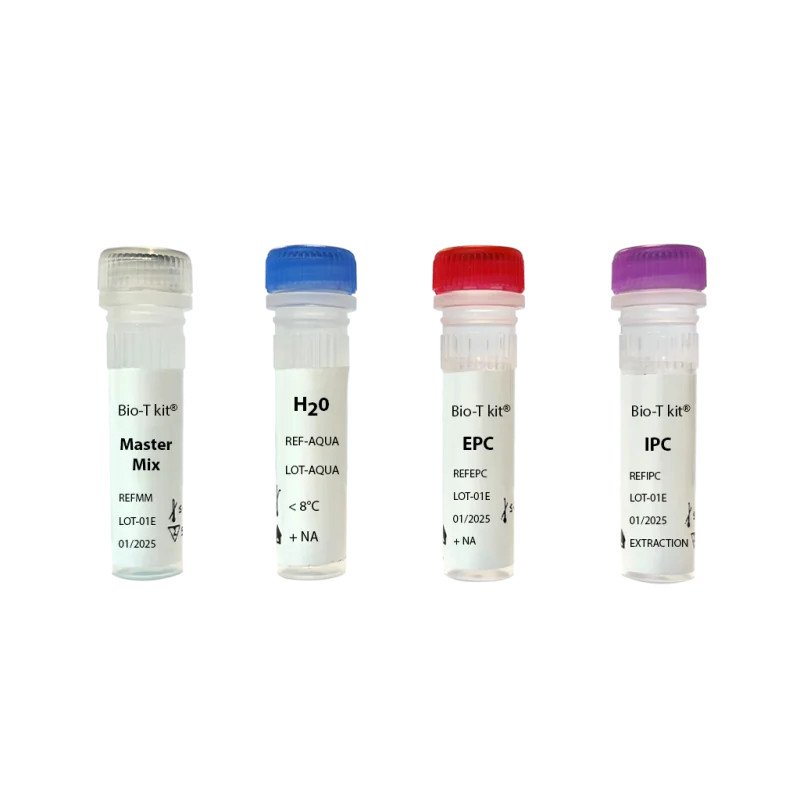
Each real-time PCR kit includes :
- Ready-to-use Master Mix (blue color)
- Positive amplification control, containing targeted pathogens - EPC
- Negative amplification control - water.
- Exogenous IPC (Internal positive control)
Each ELISA kit includes at least :
- Test plate with 12 x 8-well strips
- Sample diluent
- Negative control
- Positive control
- 100X or ready-to-use conjugate
- Conjugate diluent
- Wash solution
- Substrate
- Stop solution
- Plate adhesives
Each product comes with a certificate of analysis and detailed instructions for use to ensure optimum use and reliable results.
To ensure the integrity and efficiency of your kits, follow these storage recommendations:
Real-time PCR kits:
On receipt: Store kits at a temperature ≤ -16°C. This preserves the quality and performance of the kit components.
ELISA kits:
On receipt: Store components at 5 ± 3°C to maintain efficacy. The concentrated wash solution can be stored at room temperature, i.e. 21 ± 4°C.
By respecting these storage conditions, you ensure the reliability and optimum performance of your kits for accurate and consistent results.
- The shelf life of a PCR kit for the detection of RNA pathogens (viruses) is 12 months.
- The shelf-life of a PCR kit for the detection of DNA pathogens (viruses, bacteria, parasites) is 24 months.
- The shelf-life of an ELISA kit is 15 or 18 months.
At BioSellal, we are constantly seeking to improve our products. We regularly carry out stability studies to extend expiration dates, guaranteeing that our kits will always perform better and last longer.
Yes, absolutely! At BioSellal, we're committed to providing our customers with complete solutions to carry out their analyses under optimum conditions. That's why, for the majority of our PCR and ELISA kits, we offer in-house reference materials, guaranteeing you reliable, accurate results every time.
The quality management system implemented by BioSellal was certified ISO 9001 (version 2015) by AFNOR in June 2017 and has since been renewed for the following areas: Research and development activities, production, industrialization and sales and technical support of PCR and ELISA kits for veterinary diagnostics. BioSellal carries out several levels of quality control on product batches, as well as validation of raw materials.
All PCR kits are developed and validated to NF U47 600-2 standard. All ELISA kits are developed and validated in accordance with standards NF U47-310, NF U47-301, NF U47-300, NF U47-020, NF U47-019.
Yes, that's right! Our PCR kits are designed to be compatible with all open devices with FAM, VIC/HEX, CY5 and Texas Red/ROX reading channels. So you can use them with confidence on a wide range of thermal cyclers for optimum results.
At BioSellal, we have a particular preference for the MIC thermal cycler, the most compact, accurate and fast thermal cycler on the market.
Our various departments are always ready to answer your questions and help you. Here's how to contact us:
Sales Administration & Logistics (for all questions concerning delivery, lead times, expiry dates, batches, etc.)
Mail: contact@biosellal.com
- Phone: +33 (0)4 26 78 32 48
Sales Department (for all questions regarding information on a product, a quote, a partnership, etc.)
- Mail: commercial@biosellal.com
- Phone: +33 (0)4 26 78 32 57
Technical Support (for technical assistance on our products or for all questions following analyses)
- Mail: tech@biosellal.com
- Tel: +33 (0)4 26 78 32 48
Our dedicated teams are here to ensure you have the best possible experience with our products. We look forward to hearing from you!
Absolutely! At BioSellal, we offer customized training to maximize the use of our technologies, including real-time PCR, ELISA, sequencing and digital PCR. Whether you want to discover our products or deepen your knowledge, we're here to support you every step of the way.
All documents relating to our products are available directly on our website. Simply create an account and log in for easy access to all our documentation resources.